Next Launch
Total Students
2,609
Total Launches
683
Eggs Survived
418 61.2%
Rockets Survived
536 78.5%
Dec. 1, 2015
The Closest New Stars To Earth
by Ethan Siegel
When you think about the new stars forming in the Milky Way, you probably think of the giant star-forming regions like the Orion Nebula, containing thousands of new stars with light so bright it's visible to the naked eye. At over 400 parsecs (1,300 light years) distant, it's one of the most spectacular sights in the night sky, and the vast majority of the light from galaxies originates from nebulae like this one. But its great luminosity and relative proximity makes it easy to overlook the fact that there are a slew of much closer star-forming regions than the Orion Nebula; they're just much, much fainter.
If you get a collapsing molecular cloud many hundreds of thousands (or more) times the mass of our sun, you'll get a nebula like Orion. But if your cloud is only a few thousand times the sun's mass, it's going to be much fainter. In most instances, the clumps of matter within will grow slowly, the neutral matter will block more light than it reflects or emits, and only a tiny fraction of the stars that form--the most massive, brightest ones--will be visible at all. Between just 400 and 500 light years away are the closest such regions to Earth: the molecular clouds in the constellations of Chamaeleon and Corona Australis. Along with the Lupus molecular clouds (about 600 light years distant), these dark, light-blocking patches are virtually unknown to most sky watchers in the northern hemisphere, as they're all southern hemisphere objects.
In visible light, these clouds appear predominantly as dark patches, obscuring and reddening the light of background stars. In the infrared, though, the gas glows brilliantly as it forms new stars inside. Combined near-infrared and visible light observations, such as those taken by the Hubble Space Telescope, can reveal the structure of the clouds as well as the young stars inside. In the Chameleon cloud, for example, there are between 200 and 300 new stars, including over 100 X-ray sources (between the Chamaeleon I and II clouds), approximately 50 T-Tauri stars and just a couple of massive, B-class stars. There's a third dark, molecular cloud (Chamaeleon III) that has not yet formed any stars at all.
While the majority of new stars form in large molecular clouds, the closest new stars form in much smaller, more abundant ones. As we reach out to the most distant quasars and galaxies in the universe, remember that there are still star-forming mysteries to be solved right here in our own backyard.
With articles, activities, crafts, games, and lesson plans, NASA Space Place encourages everyone to get excited about science and technology. Visit spaceplace.nasa.gov to explore space and Earth science!
This article is provided by NASA Space Place.
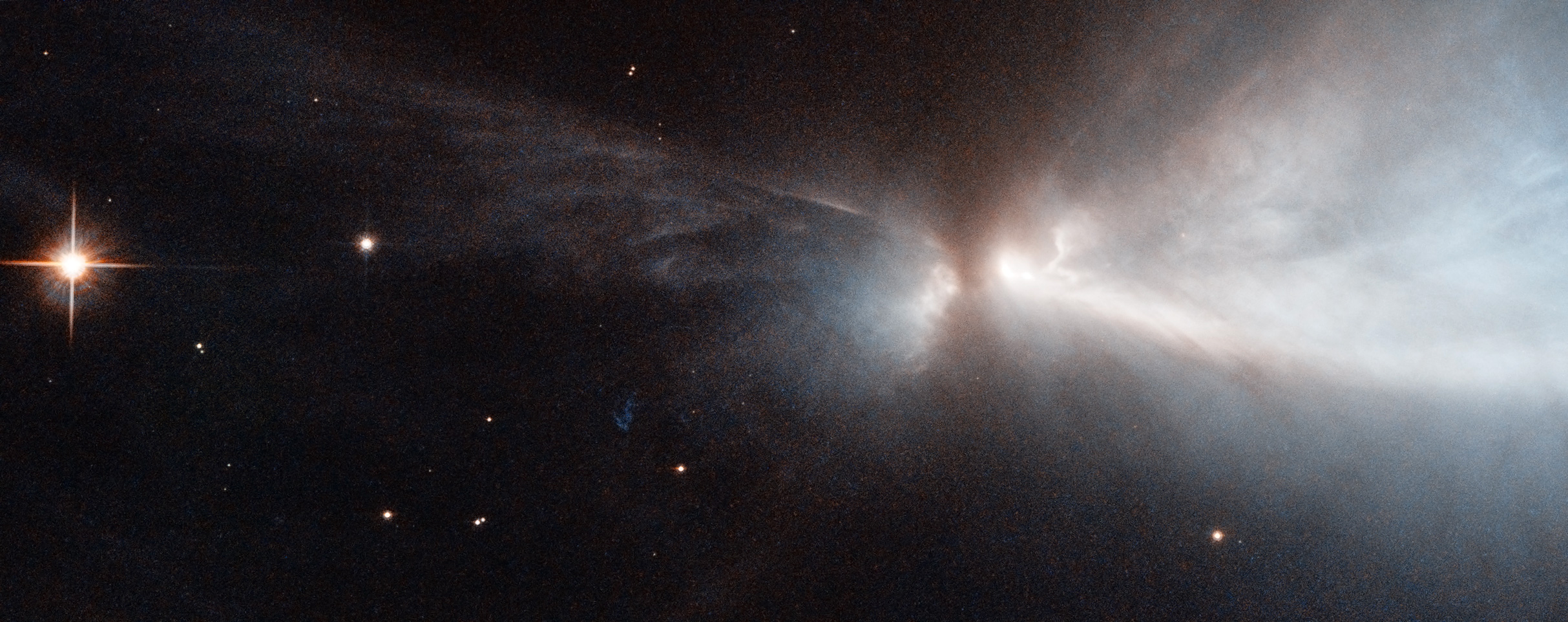 Image credit: NASA and ESA Hubble Space Telescope. Acknowledgements: Kevin Luhman (Pennsylvania State University), and Judy Schmidt, of the Chamaeleon cloud and a newly-forming star within it--HH 909A--emitting narrow streams of gas from its poles.
Image credit: NASA and ESA Hubble Space Telescope. Acknowledgements: Kevin Luhman (Pennsylvania State University), and Judy Schmidt, of the Chamaeleon cloud and a newly-forming star within it--HH 909A--emitting narrow streams of gas from its poles.
Jan. 1, 2016
The Loneliest Galaxy In The Universe
by Ethan Siegel
Our greatest, largest-scale surveys of the universe have given us an unprecedented view of cosmic structure extending for tens of billions of light years. With the combined effects of normal matter, dark matter, dark energy, neutrinos and radiation all affecting how matter clumps, collapses and separates over time, the great cosmic web we see is in tremendous agreement with our best theories: the Big Bang and General Relativity. Yet this understanding was only possible because of the pioneering work of Edwin Hubble, who identified a large number of galaxies outside of our own, correctly measured their distance (following the work of Vesto Slipher's work measuring their redshifts), and discovered the expanding universe.
But what if the Milky Way weren't located in one of the "strands" of the great cosmic web, where galaxies are plentiful and ubiquitous in many different directions? What if, instead, we were located in one of the great "voids" separating the vast majority of galaxies? It would've taken telescopes and imaging technology far more advanced than Hubble had at his disposal to even detect a single galaxy beyond our own, much less dozens, hundreds or millions, like we have today. While the nearest galaxies to us are only a few million light years distant, there are voids so large that a galaxy located at the center of one might not see another for a hundred times that distance.
While we've readily learned about our place in the universe from observing what's around us, not everyone is as fortunate. In particular, the galaxy MCG+01-02-015 has not a single known galaxy around it for a hundred million light years in all directions. Were you to draw a sphere around the Milky Way with a radius of 100 million light years, we'd find hundreds of thousands of galaxies. But not MCG+01-02-015; it's the loneliest galaxy ever discovered. Our Milky Way, like most galaxies, has been built up by mergers and accretions of many other galaxies over billions of years, having acquired stars and gas from a slew of our former neighbors. But an isolated galaxy like this one has only the matter it was born with to call its own.
Edwin Hubble made his universe-changing discovery using telescope technology from 1917, yet he would have found absolutely zero other galaxies at all were we situated at MCG+01-02-015's location. The first visible galaxy wouldn't have shown up until we had 1960s-level technology, and who knows if we'd have continued looking? If we were such a lonely galaxy, would we have given up the search, and concluded that our galaxy encompassed all of existence? Or would we have continued peering deeper into the void, eventually discovering our unusual location in a vast, expanding universe? For the inhabitants of the loneliest galaxy, we can only hope that they didn't give up the search, and discovered the entire universe.
NASA Space Place encourages everyone to get excited about science and technology with articles, activities, crafts, games, and lesson plans. Visit spaceplace.nasa.gov to explore space and Earth science!
This article is provided by NASA Space Place.
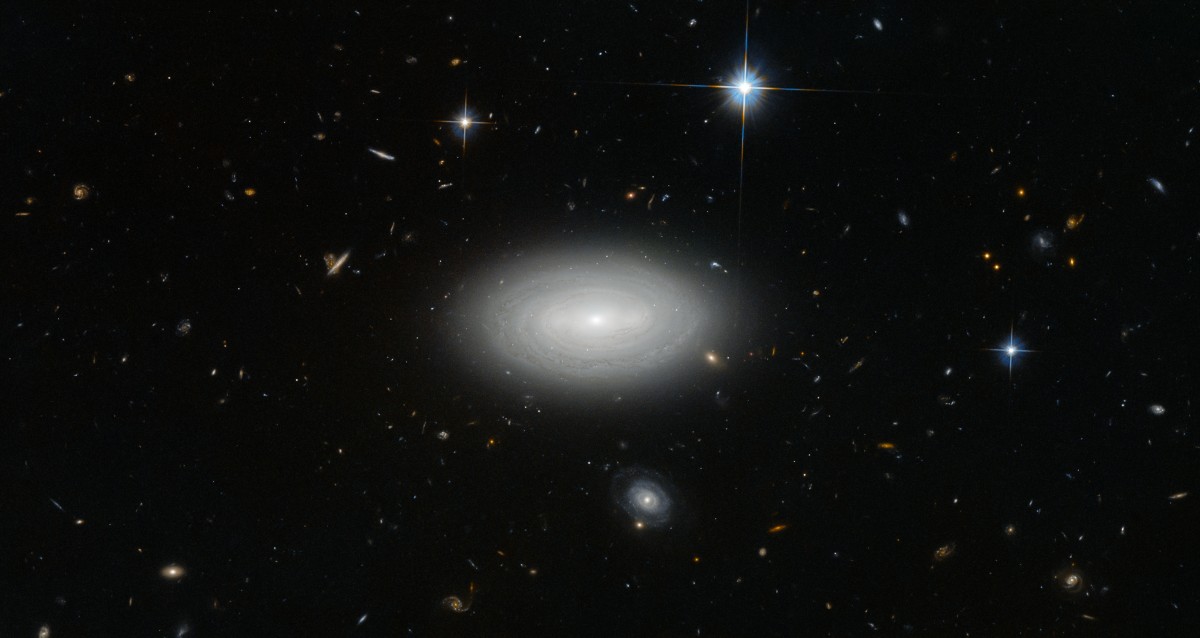 Image credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA and N. Gorin (STScI); Acknowledgement: Judy Schmidt, of the loneliest void galaxy in the known: MCG+01-02-015.
Image credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA and N. Gorin (STScI); Acknowledgement: Judy Schmidt, of the loneliest void galaxy in the known: MCG+01-02-015.
Feb. 1, 2016
The Closest New Stars To Earth
by Ethan Siegel
When you think about the new stars forming in the Milky Way, you probably think of the giant star-forming regions like the Orion Nebula, containing thousands of new stars with light so bright it's visible to the naked eye. At over 400 parsecs (1,300 light years) distant, it's one of the most spectacular sights in the night sky, and the vast majority of the light from galaxies originates from nebulae like this one. But its great luminosity and relative proximity makes it easy to overlook the fact that there are a slew of much closer star-forming regions than the Orion Nebula; they're just much, much fainter.
If you get a collapsing molecular cloud many hundreds of thousands (or more) times the mass of our sun, you'll get a nebula like Orion. But if your cloud is only a few thousand times the sun's mass, it's going to be much fainter. In most instances, the clumps of matter within will grow slowly, the neutral matter will block more light than it reflects or emits, and only a tiny fraction of the stars that form?the most massive, brightest ones?will be visible at all. Between just 400 and 500 light years away are the closest such regions to Earth: the molecular clouds in the constellations of Chamaeleon and Corona Australis. Along with the Lupus molecular clouds (about 600 light years distant), these dark, light-blocking patches are virtually unknown to most sky watchers in the northern hemisphere, as they're all southern hemisphere objects.
In visible light, these clouds appear predominantly as dark patches, obscuring and reddening the light of background stars. In the infrared, though, the gas glows brilliantly as it forms new stars inside. Combined near-infrared and visible light observations, such as those taken by the Hubble Space Telescope, can reveal the structure of the clouds as well as the young stars inside. In the Chameleon cloud, for example, there are between 200 and 300 new stars, including over 100 X-ray sources (between the Chamaeleon I and II clouds), approximately 50 T-Tauri stars and just a couple of massive, B-class stars. There's a third dark, molecular cloud (Chamaeleon III) that has not yet formed any stars at all.
While the majority of new stars form in large molecular clouds, the closest new stars form in much smaller, more abundant ones. As we reach out to the most distant quasars and galaxies in the universe, remember that there are still star-forming mysteries to be solved right here in our own backyard.
This article is provided by NASA Space Place. With articles, activities, crafts, games, and lesson plans, NASA Space Place encourages everyone to get excited about science and technology. Visit spaceplace.nasa.gov to explore space and Earth science!
This article was provided by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, under a contract with the National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
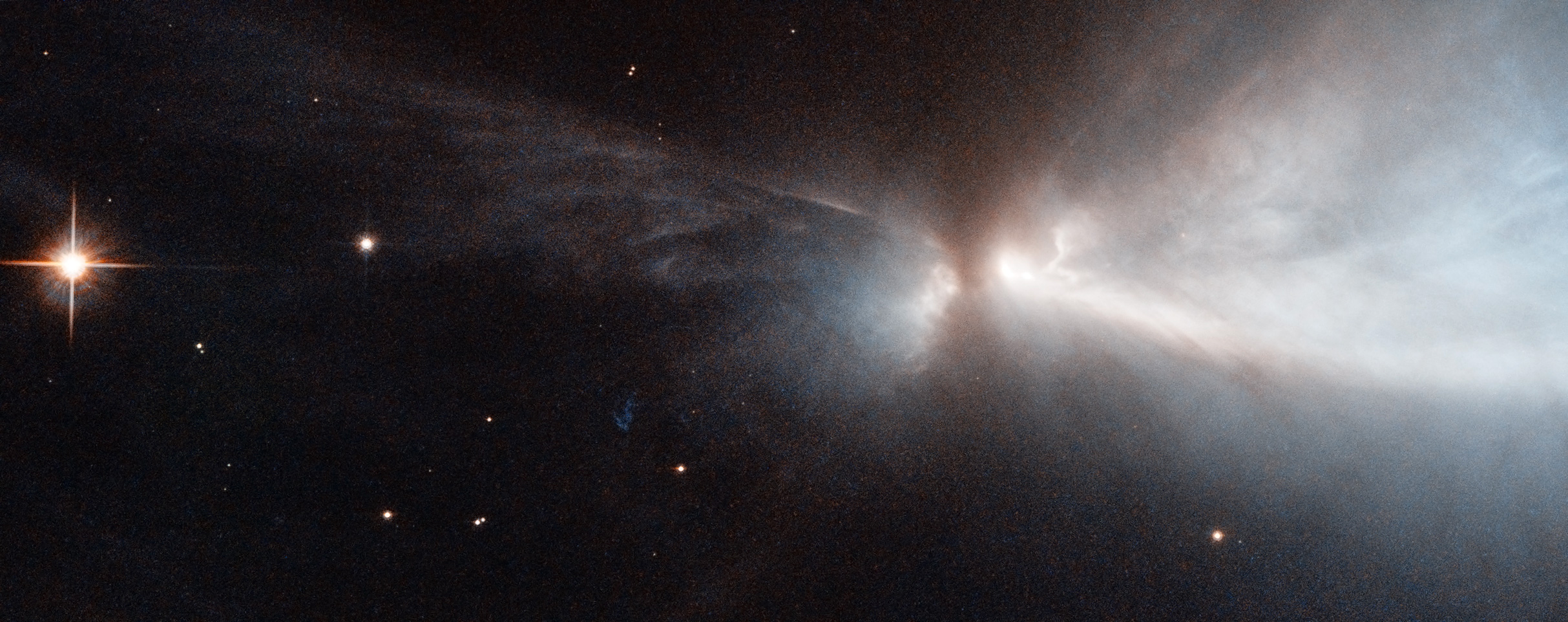 NASA and ESA Hubble Space Telescope. Acknowledgements: Kevin Luhman (Pennsylvania State University), and Judy Schmidt, of the Chamaeleon cloud and a newly-forming star within it?HH 909A?emitting narrow streams of gas from its poles.
NASA and ESA Hubble Space Telescope. Acknowledgements: Kevin Luhman (Pennsylvania State University), and Judy Schmidt, of the Chamaeleon cloud and a newly-forming star within it?HH 909A?emitting narrow streams of gas from its poles.
March 1, 2016
Gravitational Wave Astronomy Will Be The Next Great Scientific Frontier
by Ethan Siegel
Imagine a world very different from our own: permanently shrouded in clouds, where the sky was never seen. Never had anyone see the Sun, the Moon, the stars or planets, until one night, a single bright object shone through. Imagine that you saw not only a bright point of light against a dark backdrop of sky, but that you could see a banded structure, a ringed system around it and perhaps even a bright satellite: a moon. That's the magnitude of what LIGO (the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-wave Observatory) saw, when it directly detected gravitational waves for the first time.
An unavoidable prediction of Einstein's General Relativity, gravitational waves emerge whenever a mass gets accelerated. For most systems -- like Earth orbiting the Sun -- the waves are so weak that it would take many times the age of the Universe to notice. But when very massive objects orbit at very short distances, the orbits decay noticeably and rapidly, producing potentially observable gravitational waves. Systems such as the binary pulsar PSR B1913+16 [the subtlety here is that binary pulsars may contain a single neutron star, so it?s best to be specific], where two neutron stars orbit one another at very short distances, had previously shown this phenomenon of orbital decay, but gravitational waves had never been directly detected until now.
When a gravitational wave passes through an objects, it simultaneously stretches and compresses space along mutually perpendicular directions: first horizontally, then vertically, in an oscillating fashion. The LIGO detectors work by splitting a laser beam into perpendicular "arms," letting the beams reflect back and forth in each arm hundreds of times (for an effective path lengths of hundreds of km), and then recombining them at a photodetector. The interference pattern seen there will shift, predictably, if gravitational waves pass through and change the effective path lengths of the arms. Over a span of 20 milliseconds on September 14, 2015, both LIGO detectors (in Louisiana and Washington) saw identical stretching-and-compressing patterns. From that tiny amount of data, scientists were able to conclude that two black holes, of 36 and 29 solar masses apiece, merged together, emitting 5% of their total mass into gravitational wave energy, via Einstein's E = mc2.
During that event, more energy was emitted in gravitational waves than by all the stars in the observable Universe combined. The entire Earth was compressed by less than the width of a proton during this event, yet thanks to LIGO's incredible precision, we were able to detect it. At least a handful of these events are expected every year. In the future, different observatories, such as NANOGrav (which uses radiotelescopes to the delay caused by gravitational waves on pulsar radiation) and the space mission LISA will detect gravitational waves from supermassive black holes and many other sources. We've just seen our first event using a new type of astronomy, and can now test black holes and gravity like never before.
This article is provided by NASA Space Place. With articles, activities, crafts, games, and lesson plans, NASA Space Place encourages everyone to get excited about science and technology. Visit spaceplace.nasa.gov to explore space and Earth science!
This article was provided by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, under a contract with the National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
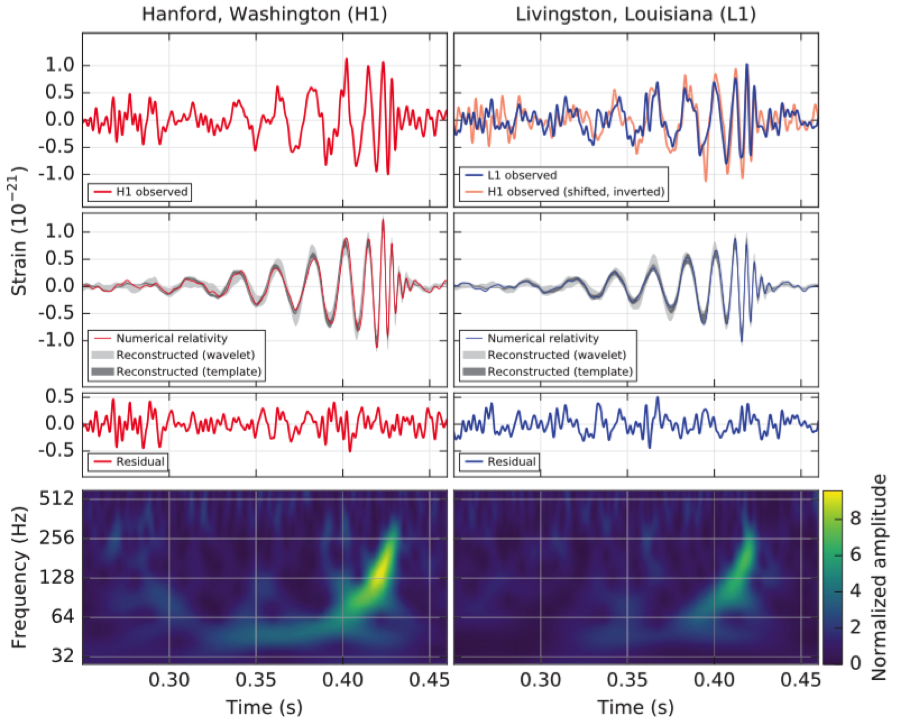 Image credit: Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Black Hole Merger B. P. Abbott et al., (LIGO Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration), Physical Review Letters 116, 061102 (2016). This figure shows the data (top panels) at the Washington and Louisiana LIGO stations, the predicted signal from Einstein's theory (middle panels), and the inferred signals (bottom panels). The signals matched perfectly in both detectors.Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Black Hole Merger B. P. Abbott et al., (LIGO Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration), Physical Review Letters 116, 061102 (2016).
Image credit: Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Black Hole Merger B. P. Abbott et al., (LIGO Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration), Physical Review Letters 116, 061102 (2016). This figure shows the data (top panels) at the Washington and Louisiana LIGO stations, the predicted signal from Einstein's theory (middle panels), and the inferred signals (bottom panels). The signals matched perfectly in both detectors.Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Black Hole Merger B. P. Abbott et al., (LIGO Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration), Physical Review Letters 116, 061102 (2016).